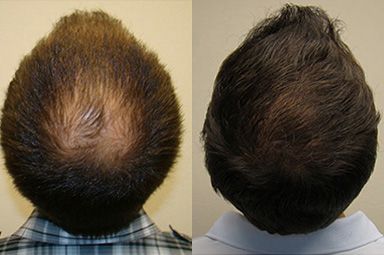
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure designed to address hair loss by relocating hair from one area of the scalp (donor site) to another (recipient site). The purpose is not merely aesthetic but also about restoring one’s confidence and self-esteem. Hair transplants can greatly improve personal well-being while not as critical as life-saving surgeries.
Table of Content
ToggleHowever, the success of a hair transplant depends on more than just moving hair—it relies on transplanting and preserving specific biological structures critical for regrowth. Just like planting a tree requires more than just putting it in the ground, proper placement of hair follicle units is crucial for healthy hair growth.
This article unpacks the anatomy of hair follicles, the procedures involved, and the importance of safeguarding these structures for optimal results.
Understanding the Anatomy of Hair Follicles
Hair follicles are intricate structures embedded in the skin, playing a crucial role in hair growth and maintenance.
The hair follicle is composed of several key parts: the root, shaft, and bulb.
- The root is the portion of the hair that lies beneath the skin’s surface, anchored within the follicle. It is surrounded by the hair bulb, a bulbous structure at the base of the follicle. The bulb is where the hair cells divide and grow, nourished by a network of blood vessels that supply essential nutrients and oxygen. This area is also home to the dermal papilla, a small, nipple-like structure that plays a pivotal role in regulating hair growth and cycling.
- The hair shaft is the visible part of the hair that extends above the skin. It is composed of three layers: the medulla, cortex, and cuticle. The medulla is the innermost layer, often absent in fine hair. The cortex provides strength and color, while the cuticle, a protective outer layer, shields the inner layers from damage.
Hair follicles are responsible for the cyclical process of hair growth, which includes three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting). - During the anagen phase, cells in the hair bulb rapidly divide, pushing the hair shaft upward and out of the follicle. This phase can last several years, determining the length of the hair.
- The catagen phase is a brief period where growth ceases, and the follicle shrinks.
Finally, during the telogen phase, the hair rests before eventually shedding, making way for new growth.
Types of Hair Transplantation
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
This method involves a meticulous process where individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area, typically the back of the scalp, using a specialised micro-punch tool.
The precision of FUE allows for the extraction of follicular units, which consist of 1 to 4 hairs, along with their essential structures such as sebaceous glands and dermal papilla cells.
These units are then carefully implanted into the recipient area, ensuring minimal scarring and a natural appearance. The key to FUE’s success largely depends on the meticulous handling and transplantation of these complete follicular units, which are crucial for healthy hair regrowth.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Unlike FUE, FUT involves removing a strip of scalp tissue from the donor area. This strip is then dissected under a microscope to isolate individual follicular units.
The main difference between FUT and FUE is the method of extraction; FUT involves a linear incision, which can result in a more noticeable scar. However, FUT allows for the transplantation of a larger number of grafts in a single session.
The extracted follicular units, containing hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and dermal papilla cells, are then transplanted into the balding areas.
The success of FUT depends on the precise removal and transplantation of these structures, ensuring they remain intact and viable for optimal hair growth.
Key Structures That Need to Be Transplanted
Hair transplantation is a sophisticated procedure and its success largely depends on the meticulous handling and transplantation of several key structures associated with hair follicles.
- Hair Follicular Unit: A hair follicular unit is a naturally occurring group of 1 to 4 hairs, along with their associated structures, such as sebaceous glands, nerves, and blood vessels. These units are the building blocks of hair transplantation, as they ensure a natural appearance and optimal growth when transplanted.
- Sebaceous Glands: Sebaceous glands play a crucial role in maintaining the health of hair follicles. These glands secrete sebum, an oily substance that lubricates the hair and scalp, preventing dryness and providing a protective barrier against external elements. Preserving sebaceous glands during transplantation is vital, as they contribute to the overall health and vitality of the transplanted hair.
- Papilla and Dermal Papilla Cells: The papilla and dermal papilla cells are integral to the growth and maintenance of healthy hair follicles. Located at the base of the hair follicle, the papilla contains a rich supply of blood vessels that deliver essential nutrients and oxygen to the hair. Dermal papilla cells are responsible for signalling hair growth and cycling.
- Hair Follicle Bulb: The hair follicle bulb is the lower part of the hair follicle, where new hair shafts are produced. It contains rapidly dividing cells that form the hair shaft and is essential for the production of new hair.
- Scalp Tissue: Scalp tissue surrounding the hair follicle provides structural support and nourishment. It contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue that are vital for the survival and function of the transplanted follicle. Transplanting scalp tissue along with the follicle helps maintain the necessary environment for hair growth, ensuring that the transplanted hair thrives in its new location.
Why Each Structure Matters in Hair Regrowth
Hair regrowth is a complex process that hinges on the integrity and functionality of various structures within the scalp. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring that hair follicles remain viable and capable of producing healthy hair.
Survival of Hair Follicles:
The survival of hair follicles is significant in maintaining hair growth. Hair follicles are intricate structures that require a stable environment to function properly. Preserving these structures involves maintaining the integrity of the follicular unit, which includes the hair shaft, sebaceous gland, and surrounding connective tissue.
Damage to any part of this unit can lead to follicle dysfunction or death, resulting in hair loss. Ensuring the survival of hair follicles involves protecting them from physical trauma, inflammation, and hormonal imbalances, which can all disrupt their normal function.
Blood Supply and Nutrients
A robust blood supply is vital for the health and growth of hair follicles. Blood vessels deliver essential nutrients and oxygen to the follicles, which are necessary for their metabolic activities. In the context of hair transplantation, ensuring adequate blood flow to transplanted follicles is critical.
Without sufficient blood supply, transplanted follicles may not survive or thrive, leading to unsuccessful hair regrowth. Techniques that enhance vascularisation, such as platelet-rich plasma therapy, can improve the survival rate of transplanted follicles by promoting better blood flow and nutrient delivery.
Cell Regeneration
Cell regeneration is a key factor in hair follicle health and hair regrowth. Dermal papilla cells, located at the base of the hair follicle, play a pivotal role in regulating hair growth cycles. These cells interact with surrounding epithelial cells to initiate and sustain the growth phase of the hair cycle.
The regenerative capacity of dermal papilla cells is influenced by their ability to communicate with other cells and respond to growth signals. Additionally, the surrounding tissue, including the extracellular matrix, provides structural support and biochemical signals that facilitate cell regeneration.
Techniques to Improve Graft Survival and Hair Growth
In the realm of hair restoration, ensuring the survival and growth of transplanted follicles is significant. Advanced techniques and tools have been developed to enhance the success rates of hair transplants, making them more effective and reliable.
One of the most significant advancements is the use of robotic hair transplants. These systems utilise precision robotics to extract and implant hair follicles with minimal trauma, reducing the risk of damage and increasing the likelihood of graft survival. The accuracy of robotic systems allows for optimal placement of follicles, which is crucial for natural-looking results and improved growth rates.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is another innovative technique that has gained popularity. PRP involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp, which can stimulate hair growth and improve the health of transplanted follicles. The growth factors in PRP promote healing and enhance the survival of grafts, making it a valuable adjunct to hair transplant procedures.
Importance of Post-Transplant Care
Post-transplant care is equally important in ensuring the longevity and success of hair restoration.
Patients are advised to follow specific guidelines to protect the newly transplanted structures. This includes avoiding direct sunlight, refraining from strenuous activities, and using prescribed medications to reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
Proper care during the recovery phase can significantly impact the overall outcome of the transplant.
Maximising Survival Rates
Graft storage and handling are critical components that influence survival rates.
During the transplant procedure, follicles are temporarily stored in a specialised solution that maintains their viability. The temperature and environment in which grafts are kept play a crucial role in preserving their health.
Techniques such as hypothermic storage and the use of nutrient-rich solutions help maximise the survival of grafts before they are implanted.
Factors Affecting the Growth of Transplanted Hair
Several key factors play a crucial role in the growth of transplanted hair:
- Genetic Factors: Genetics significantly impact the growth success of transplanted follicles. Individuals with a family history of robust hair growth are more likely to experience successful outcomes post-transplant. Genetic predispositions can determine the density, texture, and growth rate of the transplanted hair.
Moreover, genetic factors can influence the susceptibility to conditions like androgenetic alopecia, which may affect the longevity and health of the transplanted hair. - Scalp Condition: The health of the scalp is paramount for the survival of transplanted hair follicles. A well-nourished, clean, and adequately hydrated scalp provides an optimal environment for the follicles to anchor and thrive.
Conditions such as scalp psoriasis, dermatitis, or excessive oiliness can impede the healing process and affect the growth of new hair. - Post-Surgical Care: Aftercare is crucial to ensure that transplanted structures grow optimally. Patients are typically advised to avoid strenuous activities, direct sunlight, and harsh hair products in the initial weeks following surgery.
Gentle washing and the use of prescribed medications or topical treatments can aid in reducing inflammation and promoting healing. - Immune Response: The body’s immune response plays a significant role in the acceptance of transplanted follicles. While hair transplants generally involve the patient’s hair, reducing the risk of rejection, the immune system’s reaction can still affect the outcome. Inflammation and immune-mediated responses can hinder follicle survival.
Common Challenges in Transplanting Structures
Transplanting structures, particularly in the context of hair restoration, present several challenges that can affect the overall success of the procedure.
- Graft failure can occur due to various reasons, including poor handling of the grafts, inadequate blood supply, or infection. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to ensure that the grafts are handled with utmost care during the extraction and implantation processes. Maintaining a sterile environment and ensuring proper hydration of the grafts can also significantly reduce the chances of failure.
- Another critical factor influencing the success of a hair transplant is the hair growth cycle. Hair follicles undergo phases of growth, rest, and shedding, which can affect the visible results of the transplant. Understanding these cycles is essential for timing the procedure and setting realistic expectations for hair regrowth.
- Choosing an experienced surgeon is important for optimal follicle preservation. An adept surgeon will have the skills necessary to extract and implant follicles with precision, minimising trauma and ensuring the highest survival rate of the grafts. Their expertise ensures better outcomes by managing procedural complexities and tailoring the approach to each patient’s needs.
Emerging Technologies in Hair Transplants
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence and robotics have significantly enhanced the precision of follicle extraction and transplantation processes.
AI algorithms are now capable of analysing hair patterns and densities to optimise the selection and placement of hair follicles, while robotic systems provide unparalleled accuracy and speed in surgical procedures.
Looking ahead, future trends in hair transplant technology are poised to revolutionise the field further. Stem cell therapy is being explored as a technique to regenerate hair follicles, potentially offering a renewable source of hair for transplantation.
Follicle cloning, another promising avenue, involves replicating hair follicles in a laboratory setting, which could dramatically increase the availability of transplantable hair.
Additionally, genetic manipulation techniques are being developed to improve the quality and longevity of transplanted hair, potentially allowing for personalised treatments that cater to individual genetic profiles.
Conclusion
Achieving successful hair regrowth through transplantation comes down to carefully selecting and transplanting the right structures. Preserving and precisely placing the essential components of hair follicles is key to creating natural, lasting results.
With ongoing advancements in techniques, we’re getting better at maintaining the integrity of these vital structures, ensuring that each procedure is as effective as possible. This progress not only improves the aesthetic outcomes but also helps individuals regain their confidence and feel great about themselves again.
The future of hair transplantation is exciting—better methods and a deeper understanding of how follicles work mean even more satisfying results for anyone looking to restore their hair.
Remember, your journey to a fuller, healthier hairline is well within reach!
To learn more about FUE Hair Transplant or book a consultation, visit Hair Transplant Harley St. Healthcare.


